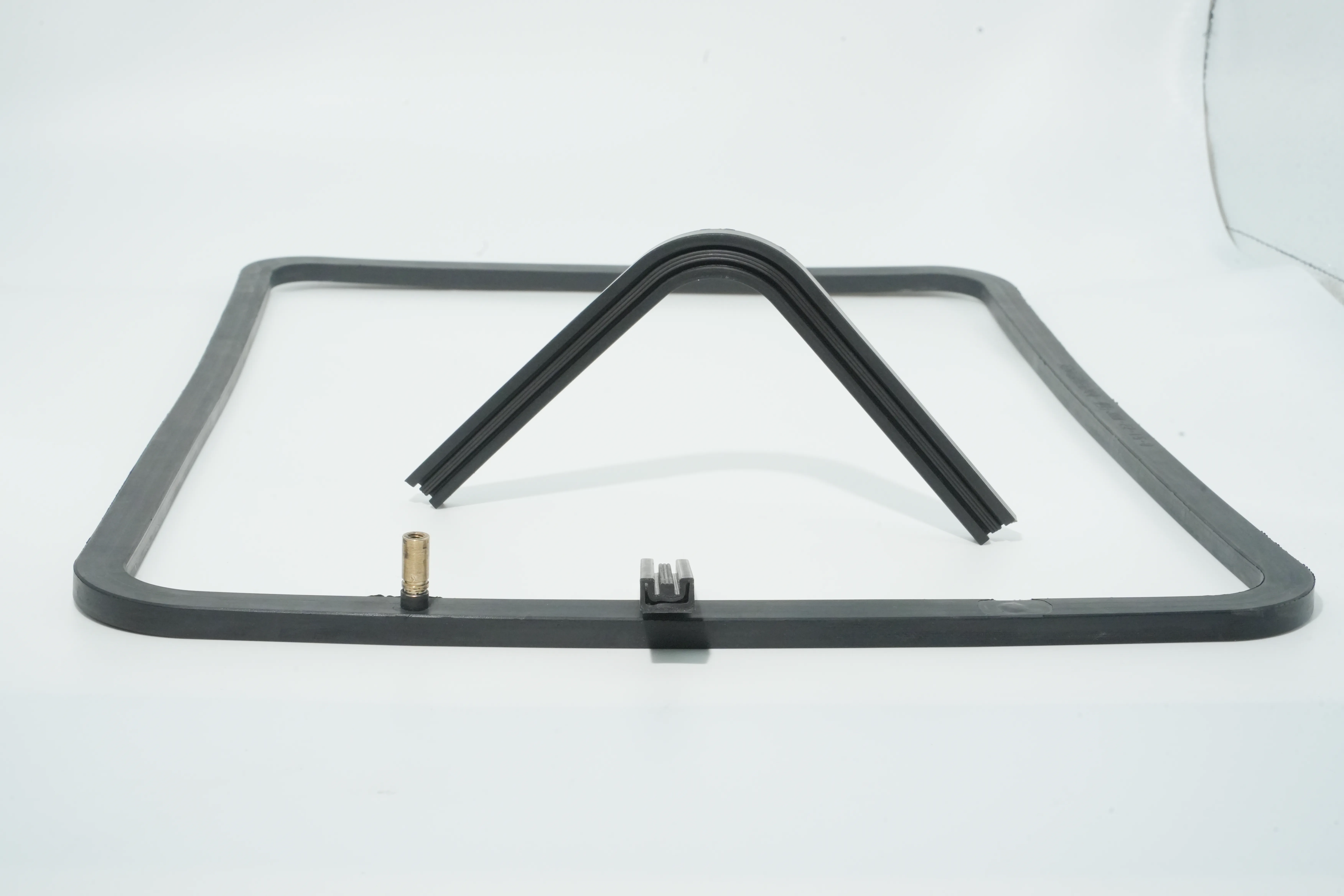
General Inflatable Seal Questions
What is an inflatable seal and how does it work?
An inflatable seal is an elastomeric sealing device that expands when pressurized with air or other gases to form an airtight or liquid-tight barrier between two surfaces. Unlike traditional static seals, inflatable seals can be activated on demand, allowing for clearance during non-sealed states (like when opening/closing doors or hatches). When inflated, they expand to fill gaps and accommodate surface irregularities, providing exceptional sealing in applications where conventional seals would fail.
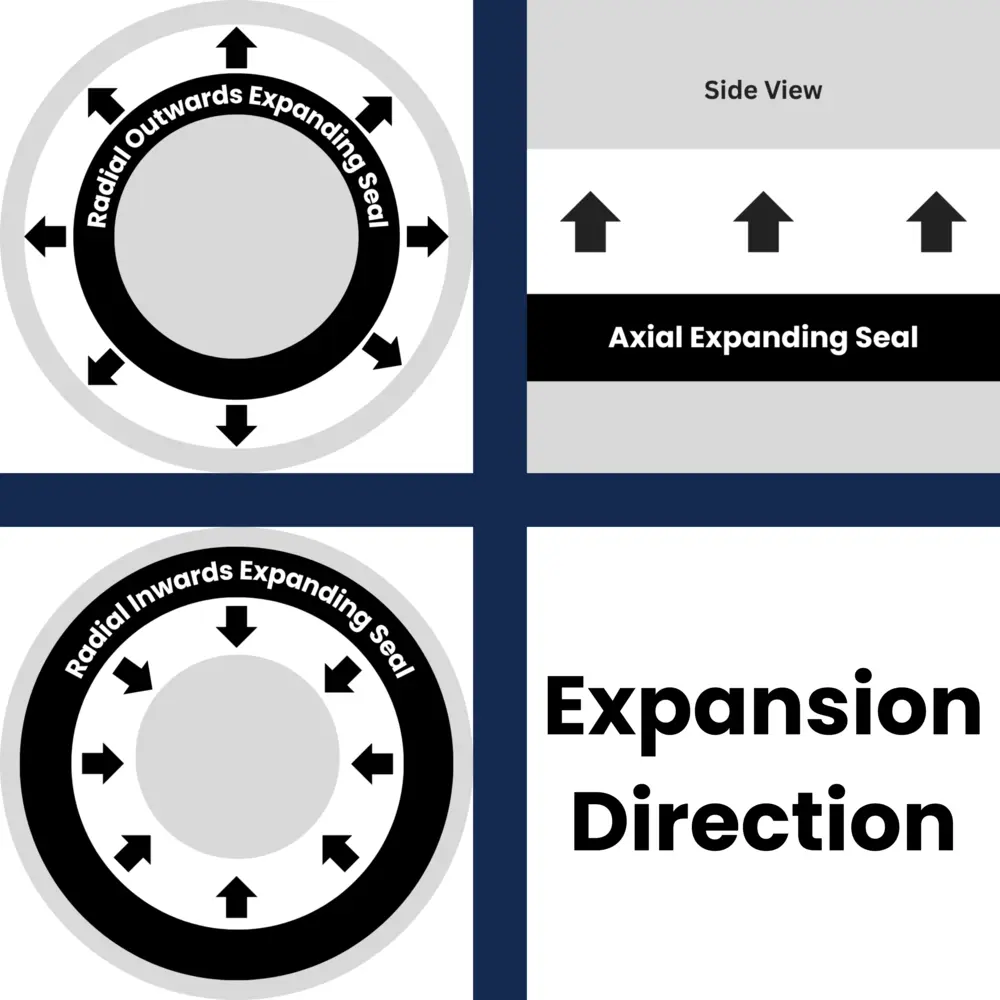
The seal works by introducing compressed air or gas through an inlet valve, causing the flexible elastomer body to expand in a controlled direction (axially, radially, or multi-directionally) until it contacts and seals against the mating surface. When the application requires access, the air pressure is released, and the seal contracts to its original shape.

What are the main advantages of inflatable seals over conventional seals?
Inflatable seals offer several significant advantages over conventional static seals:
- On-demand activation: Only engage when sealing is needed, reducing wear during non-sealed states
- Gap accommodation: Can seal across larger gaps and tolerances than static seals
- Surface irregularity compensation: Conform to uneven surfaces and minor misalignments
- Reduced friction: Minimal contact when deflated, allowing doors/hatches to open without dragging across seal surfaces
- Multiple sealing directions: Available in designs that expand axially, radially, or in multiple directions
- Greater pressure capabilities: Can create higher sealing forces than static seals of similar size
- Space efficiency: Can achieve larger sealing areas while occupying less space in the deflated state
In what industries and applications are inflatable seals typically used?
Inflatable seals are versatile sealing solutions used across numerous industries, including:
- Pharmaceutical & Medical: Sterilization chambers, containment systems, isolation units
- Food & Beverage: Processing equipment, mixing vessels, ovens, freezers
- Aerospace: Aircraft doors, cargo hatches, test chambers, pressurized compartments
- Automotive: Paint booths, assembly fixtures, test equipment
- Nuclear: Containment systems, glove boxes, transfer chambers
- Marine: Watertight doors, hatches, dock seals
- Defense: Military vehicles, NBC (Nuclear, Biological, Chemical) protection systems
- Industrial: Processing equipment, autoclaves, ovens, freeze dryers
- Transportation: Railway doors, bus doors, specialized vehicle seals
- Semiconductor: Process equipment, vacuum chambers, clean rooms
Common applications include sealing doors, hatches, chambers, lids, covers, windows, viewports, and any scenario requiring a reliable, controllable seal with minimal friction during opening and closing operations.